Articles
Challenges
MyScore
Your creditworthiness
MyOffers
Your personal offers
Comparator
Offers comparison

Learn, earn crystals and take control of your finances. This fun form of learning will help you become an expert with financial freedom and a better future. Start a new game, start a new life.
Empower your financesAccept the challenge and start your journey now!
With a Personal Score, you can find out how financial institutions will assess your creditworthiness. Get a free assessment including recommendations now.
Find out your score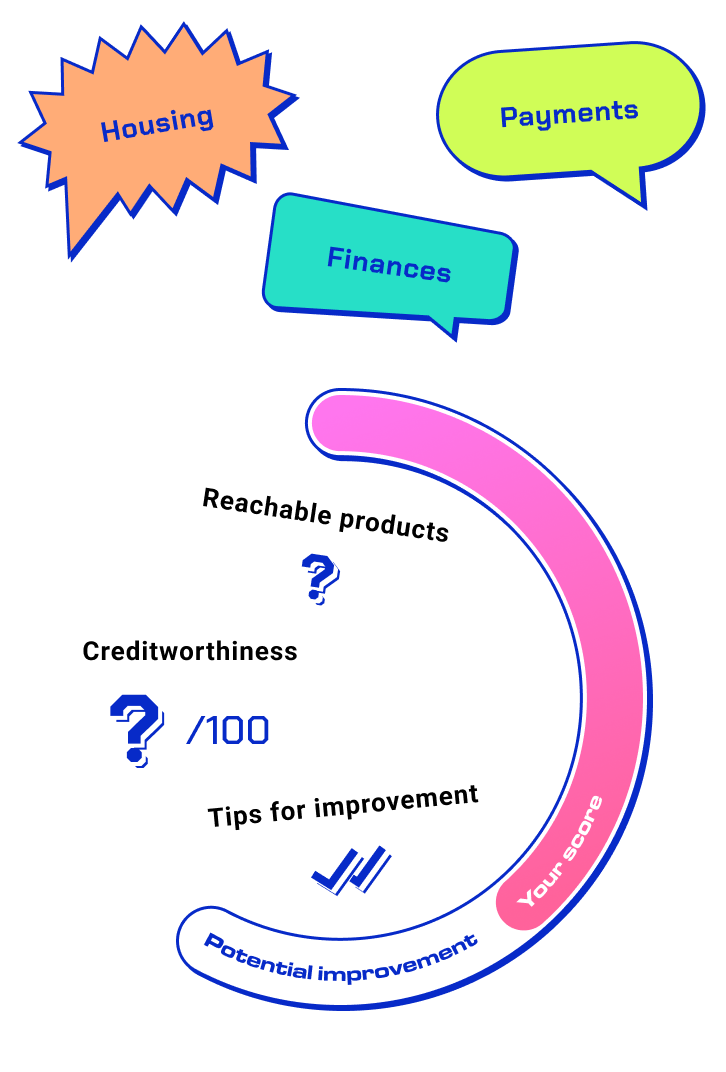

PeraWise is a financial education portal with gaming features. It offers you a wide variety of articles with quizzes (so called challenges) that improve and test your financial knowledge. By completing this process, you earn valuable crystals, which you can use for additional tries and other possibilities.
You can also check your personal creditworthiness in three levels. That reflects your financial status from the financial institutions’ point of view. That will help you to assess your situation. PeraWise will also give you advices how to improve your personal scoring.




All of that will help you become an expert with financial freedom

This is you, that's pretty easy. A hero fighting through the challenge to financial freedom.

And this is your main enemy. The incomprehensible financial world and greedy financial institutions that need to be defeated with your knowledge.


